System-Based Protection Testing or Dynamic Protection Testing
The Protection Testing Overview: From Technological Evolution to Functional Assessment
Correct protection operation is vital for power system integrity. Historically, we have witnessed a profound technological evolution, moving from electromechanical relays to static and microprocessor-based devices, reaching today’s modern IEDs (Intelligent Electronic Devices). With this evolution, protection functions have become significantly more complex, demanding testing methodologies that simulate real-world operating scenarios to ensure asset safety.
In this context, standards such as IEC 60255 establish minimum requirements for functional assessment and documentation, promoting a standardization of results essential for engineering. This rigor applies to type tests, firmware validation, and new equipment approval. Fundamentally, this assessment rests on two pillars: static testing, focused on settings precision, and dynamic testing, focused on global performance under power system stresses.
Comparison: Static (Settings-Based) vs. Dynamic (System-Based) Testing
Ensuring IED reliability requires two complementary approaches. Static testing focuses on verifying parameterization and the accuracy of protection functions. It uses current and voltage signal injections to evaluate whether the IED actuation falls within defined tolerances, focusing solely on the device under test.
Dynamic testing, on the other hand, focuses on system performance. It reproduces real grid conditions, including frequency variations, load changes, and fault dynamics. While static testing tells you if the IED is “well-calibrated,”dynamic testing answers whether the IED will “operate correctly” given the full complexity of the electrical system.
Static Testing: Precision and Productivity with CTC
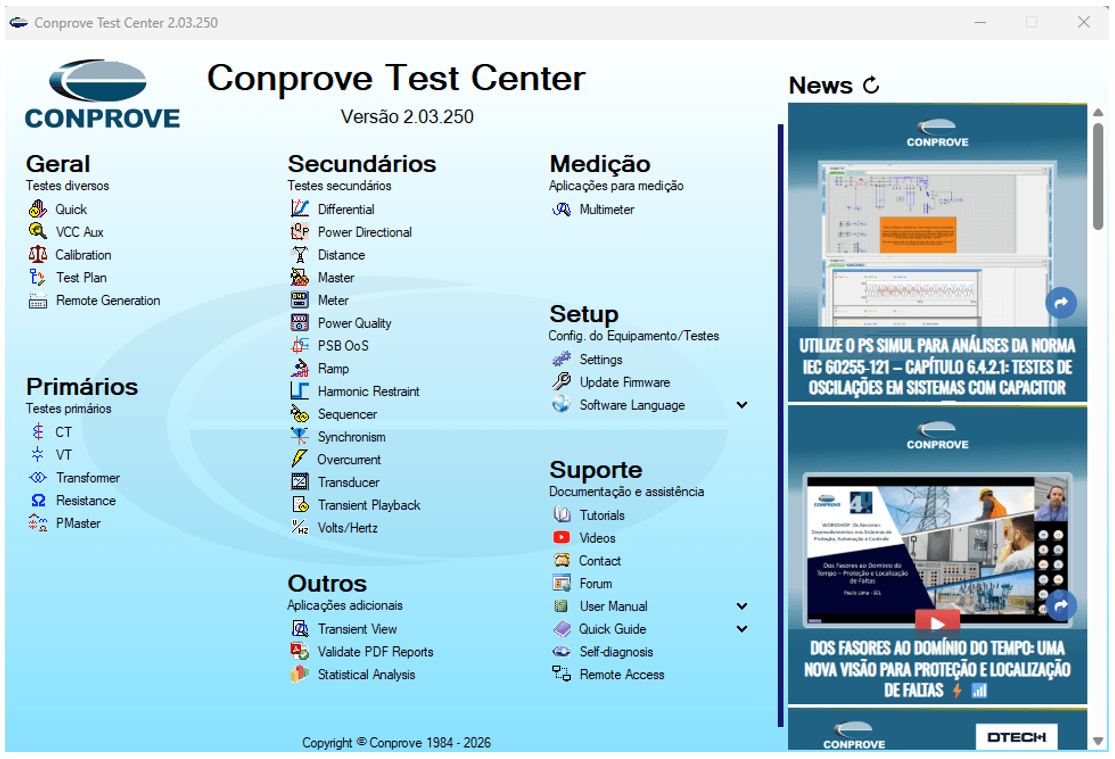
For validating IED settings and accuracy, we present the CTC – Conprove Test Center. This software is the definitive platform for automated testing, consolidating various protection functions into a single environment.
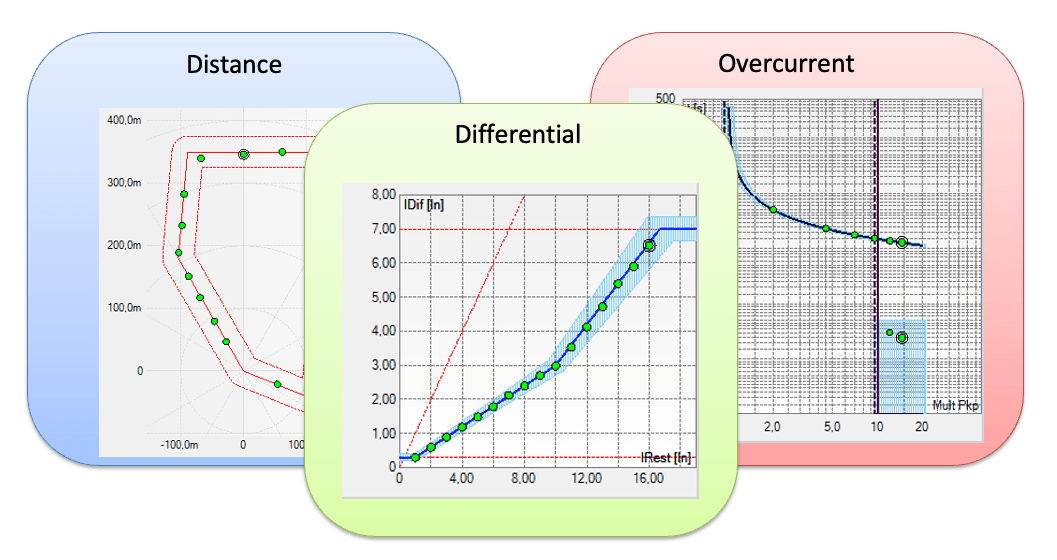
- Function Versatility: Performs automated tests for Overcurrent (50/51), Distance (21), Differential (87), Synchronism (25), and more.
- Test Reports: Allows the creation of comprehensive, user-friendly, and editable reports, simplifying documentation for the user.
- Operational Efficiency: Drastically reduces testing time by automating the plotting of curves and operating zones, reliably evaluating if the device will operate exactly as parameterized.
Dynamic Testing: Holistic Approach with PS Simul
When the goal is to evaluate protection performance against the actual power system, the solution is PS Simul. This software is dedicated to power system modeling and electromagnetic transient simulation.
- Detailed Modeling: Structures complex systems through a vast library of blocks, including transmission lines, synchronous machines, transformers with saturation, and ideal sources.
- Transient Simulation: Unlike static tests, PS Simul reproduces phenomena such as DC offset, variable frequencies, and the effect of CT saturation on protection.
- Holistic Analysis: Evaluates the systemic view of the fault, ensuring protection acts correctly even under extreme conditions that pure sine waves cannot represent.
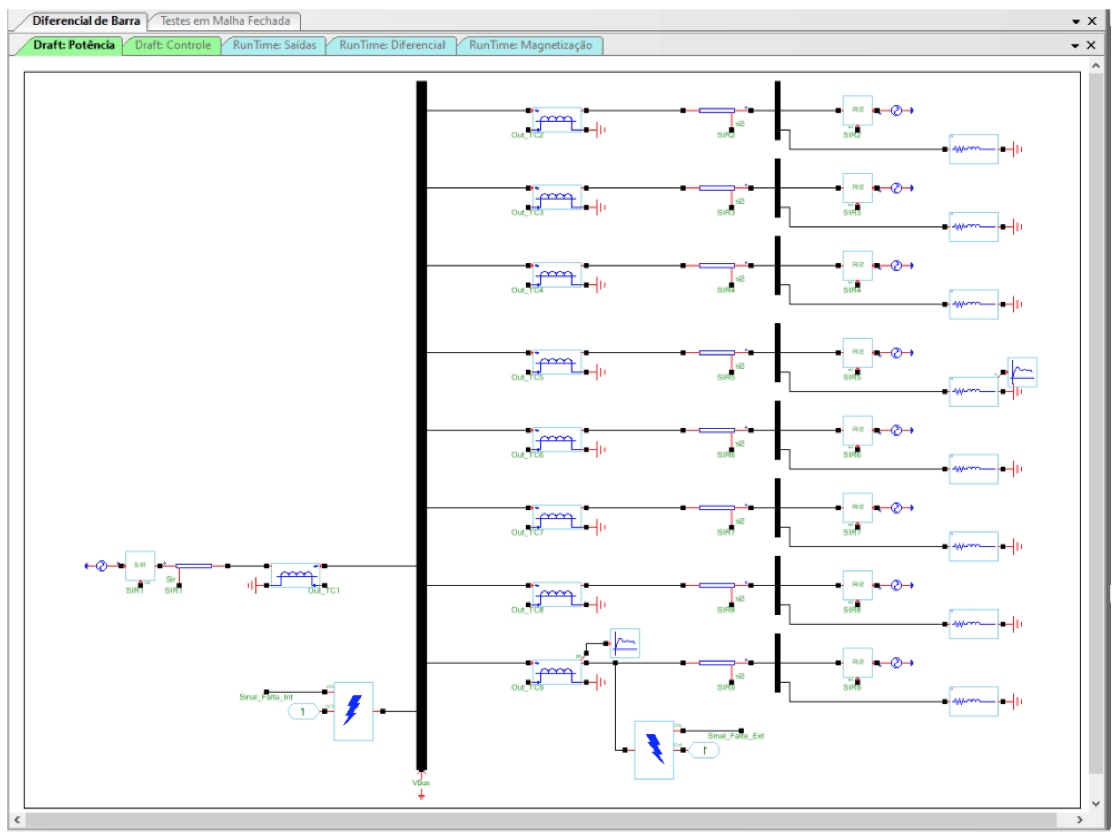
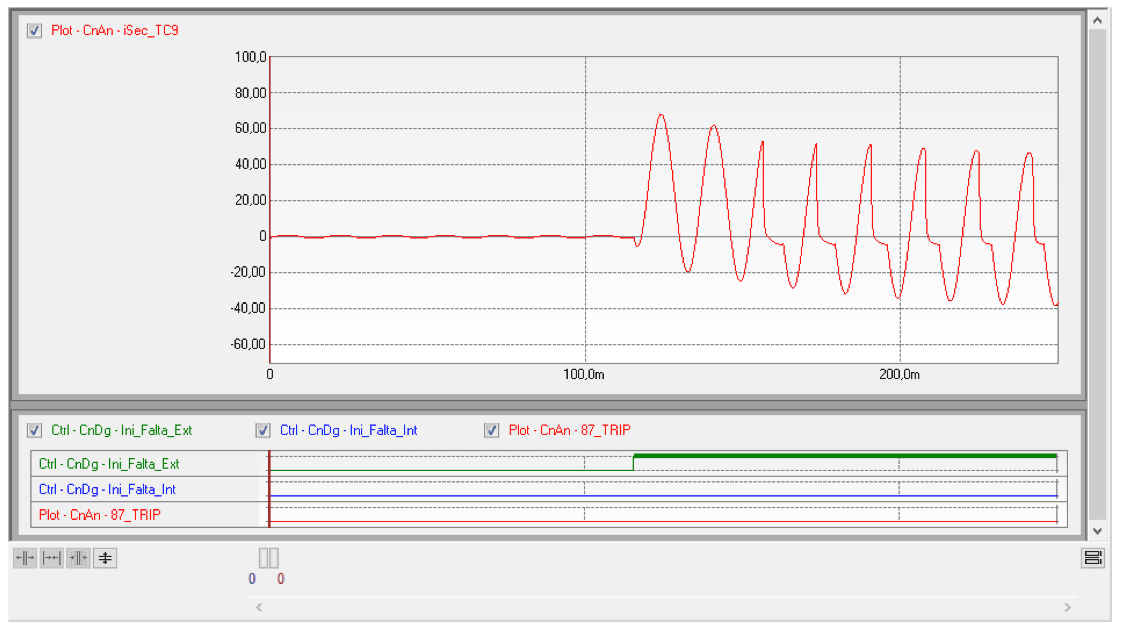
The Importance of a Holistic View
Robust protection requires a holistic view, where the IED is not seen in isolation but as an integral part of a complex system. Fault analysis cannot ignore electromagnetic transients, such as current transformer (CT) saturation and high-frequency oscillations caused by switching or discharges.
These phenomena can lead to misoperations. Ignoring transient contributions means performing an incomplete test, as relay behavior under a pure sinusoidal regime is drastically different from its response to a waveform distorted by CT saturation, for example.
Closed-Loop Simulation with PS Simul
A major advancement in protection testing comes from closed-loop tests using CONPROVE PS Simul electromagnetic transient simulation software and CONPROVE test sets. Unlike open-loop tests, closed-loop enables real-time interaction between the test set and the IED.
In this setup, PS Simul, together with the test sets, simulates the target system, controlling signal generation and reading IED responses via binary contacts or GOOSE. The defining feature of these tests is feedback: the device under test (IED) not only receives simulated signals (voltages and currents) but also interacts with the modeled system, influencing its behavior and being influenced in return.
To enable this advanced approach, CONPROVE provides complete solutions integrating hardware and software with high performance, flexibility, and precision. Recommended products include:
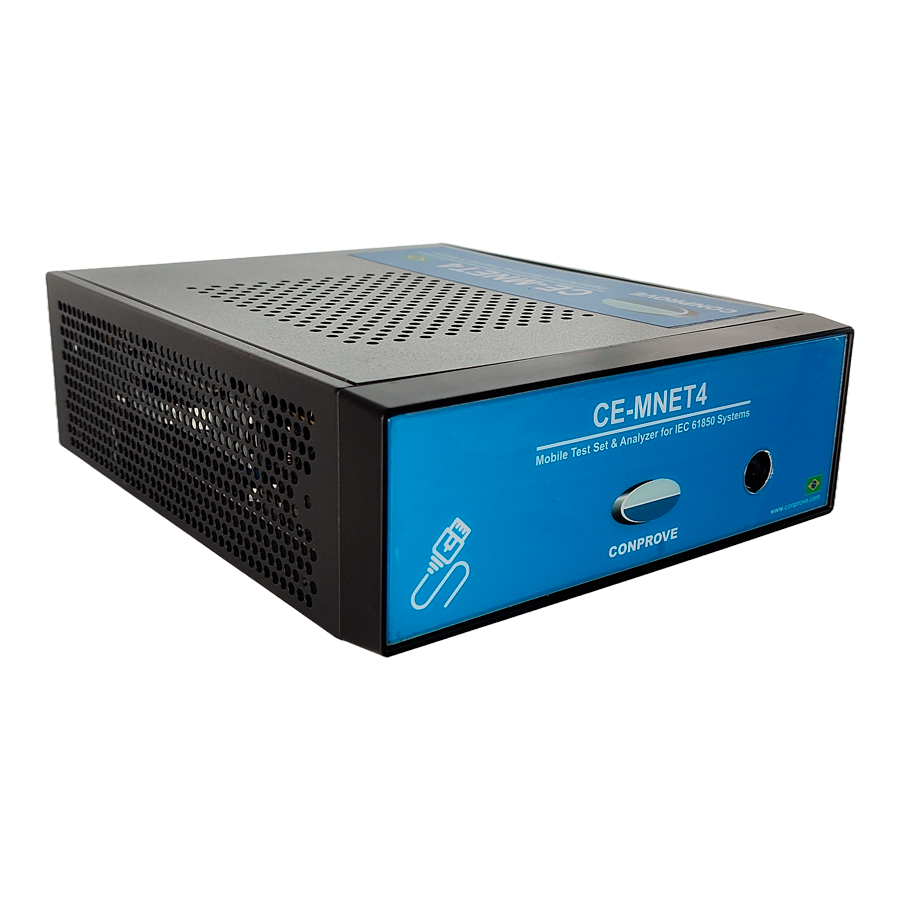
- CE-MNET4: Versatile tool capable of performing network tests and diagnostics in IEC 61850 / IEC 61869 digital substations.
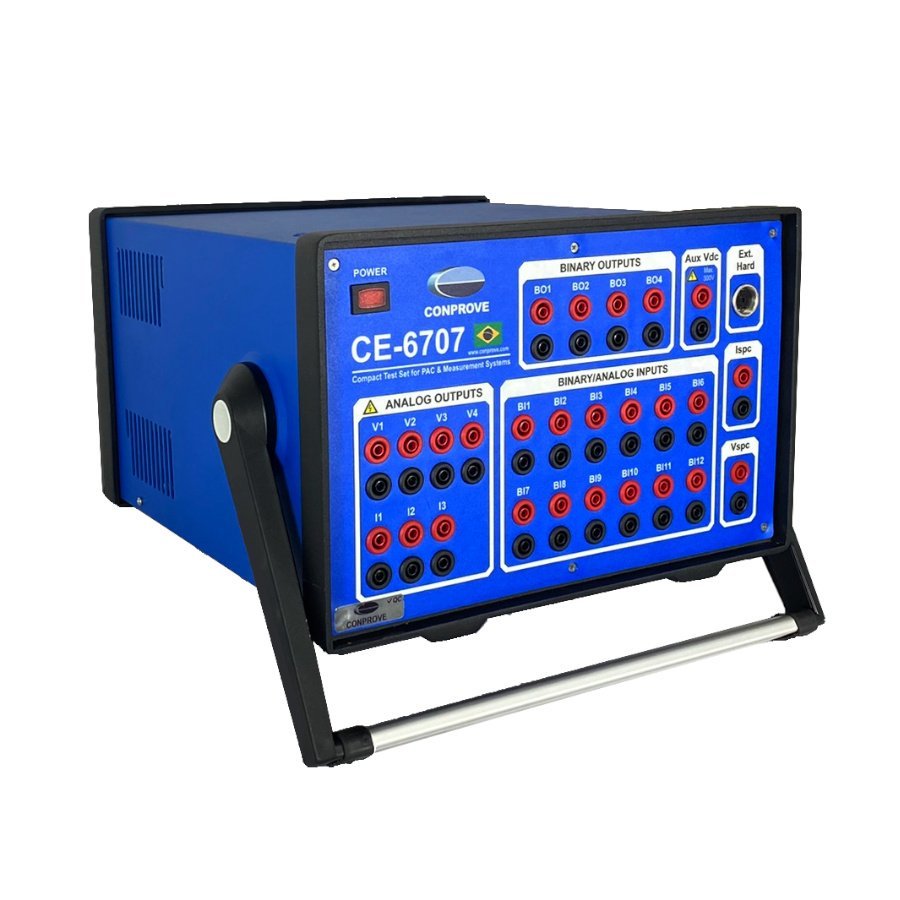
- CE-6707: Portable instrument, ideal for both field and laboratory.
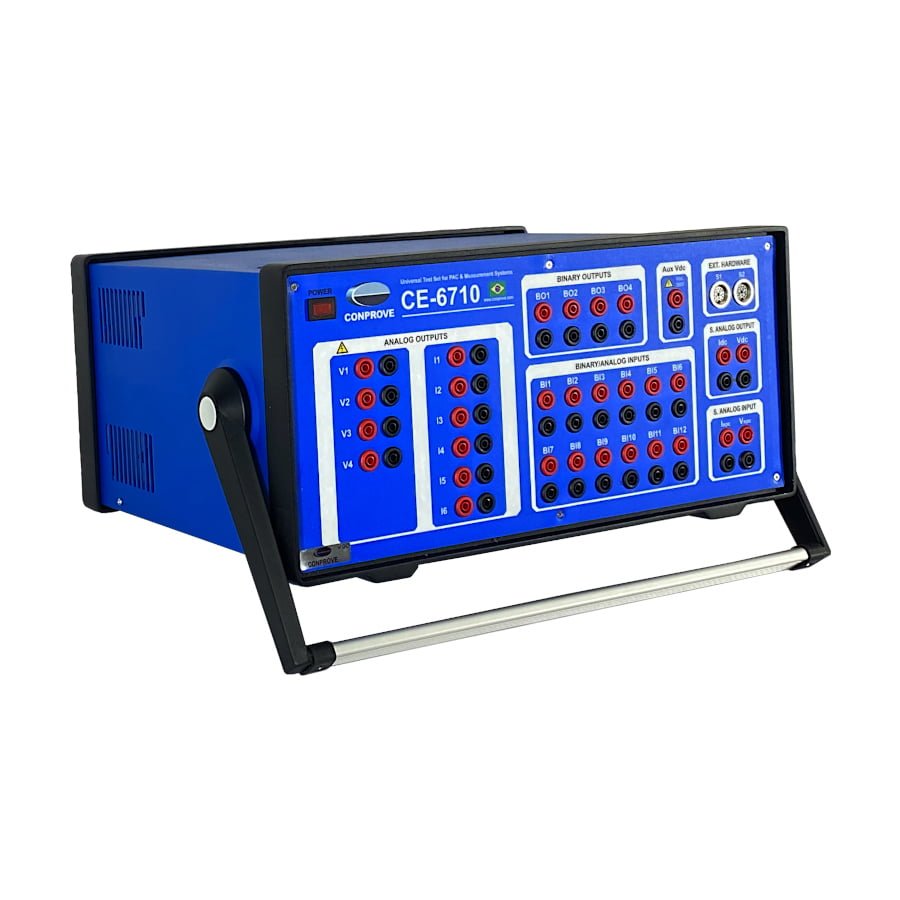
- CE-6710: Universal multifunction tester with 6 current channels and 4 voltage channels.
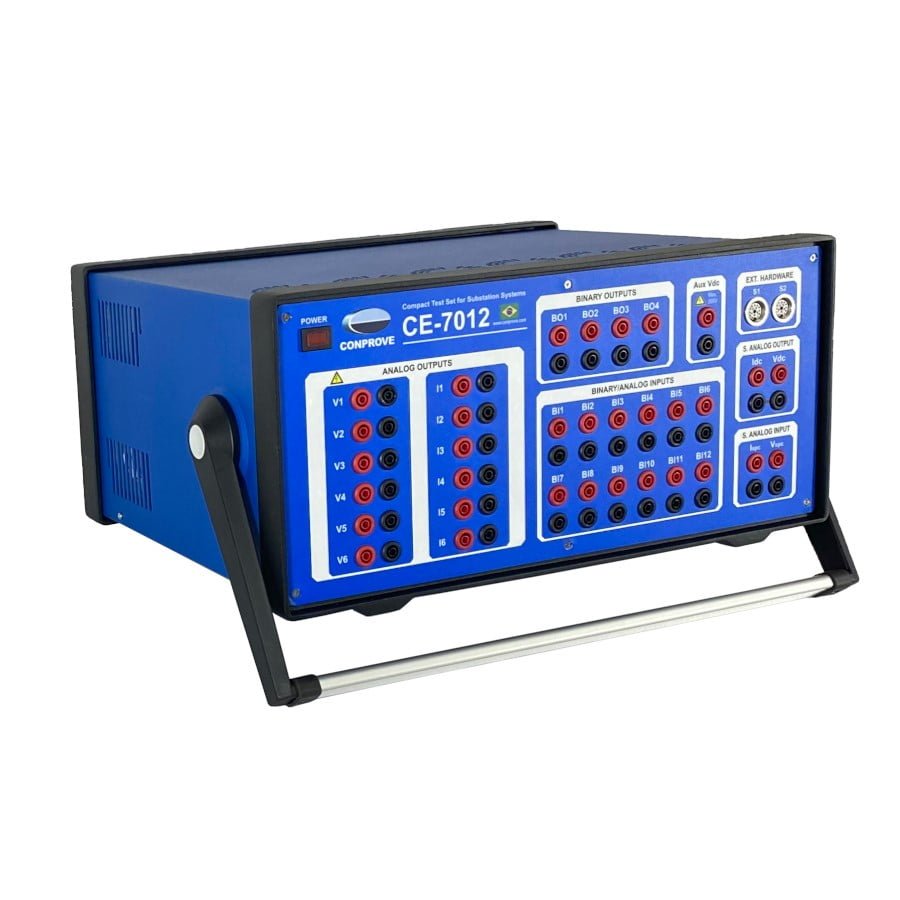
- CE-7012: Universal multifunction tester with 6 current channels and 6 voltage channels. Capable of performing primary-level tests.
- PS Simul: Software for Power System Modeling and Electromagnetic Transient Simulation.
End-to-End Testing with CE-7012: Bench Innovation
Traditionally, line protection tests involving two terminals (end-to-end) require GNSS (GPS) synchronization to ensure synchronicity between test sets at the trigger moment. However, advanced solutions like the CE-7012 offer a disruptive alternative for bench testing.
Due to its hardware architecture, which provides 6 voltage channels and 6 current channels, the CE-7012 can simulate both terminals of a transmission line simultaneously in the lab. Since outputs are generated by the same internal equipment clock, the need for external synchronization is eliminated. This drastically simplifies the logistics of testing teleprotection schemes and line differential logic, allowing engineering teams to validate interoperability and performance of two IEDs within a controlled bench environment, with zero synchronization error between ends.
This set of methodologies, from fine settings verification to dynamic closed-loop simulation, raises the safety standard of substations, ensuring PACS responds accurately to the challenges imposed by the technological evolution of protection, automation, and control systems.