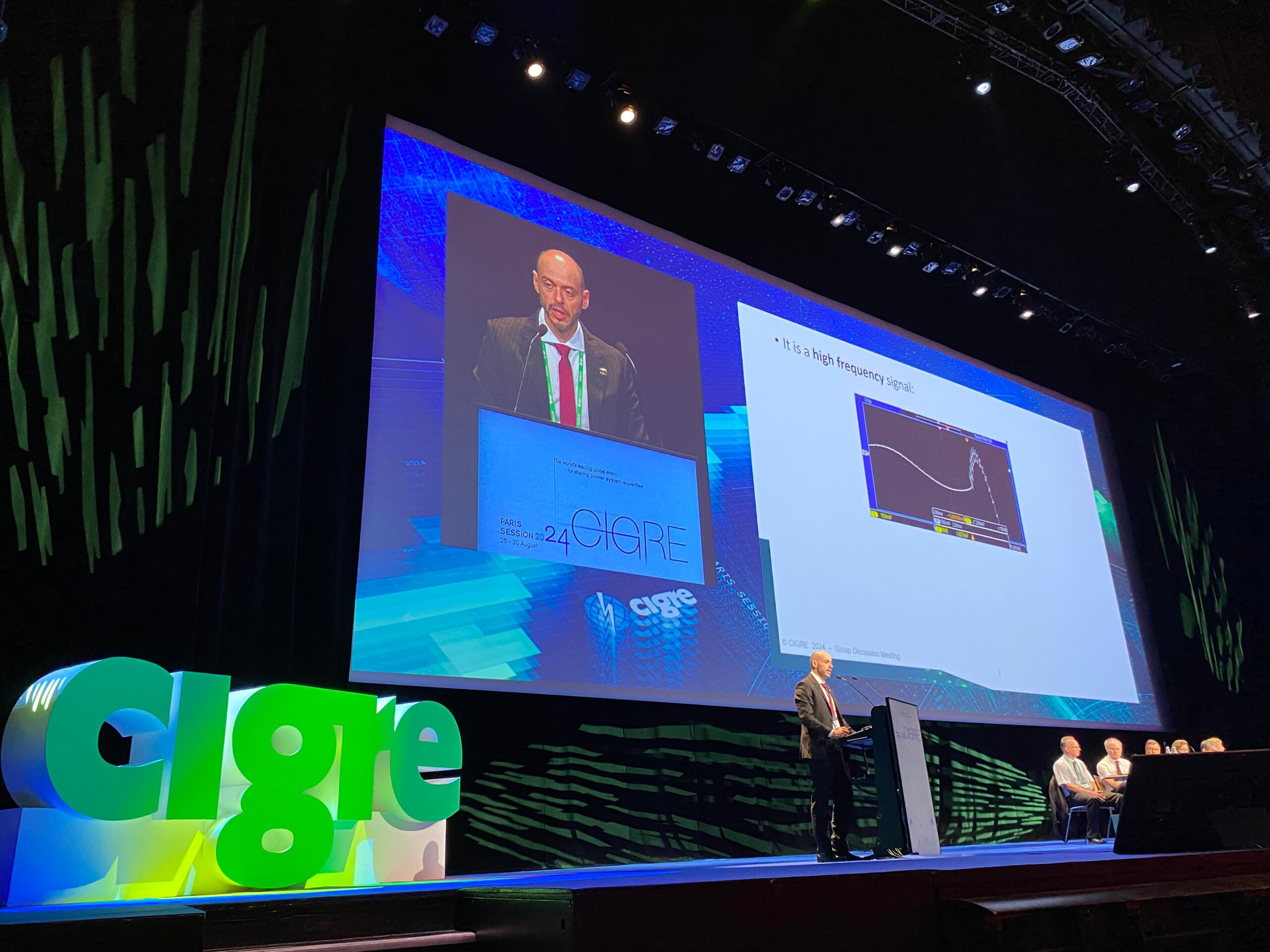
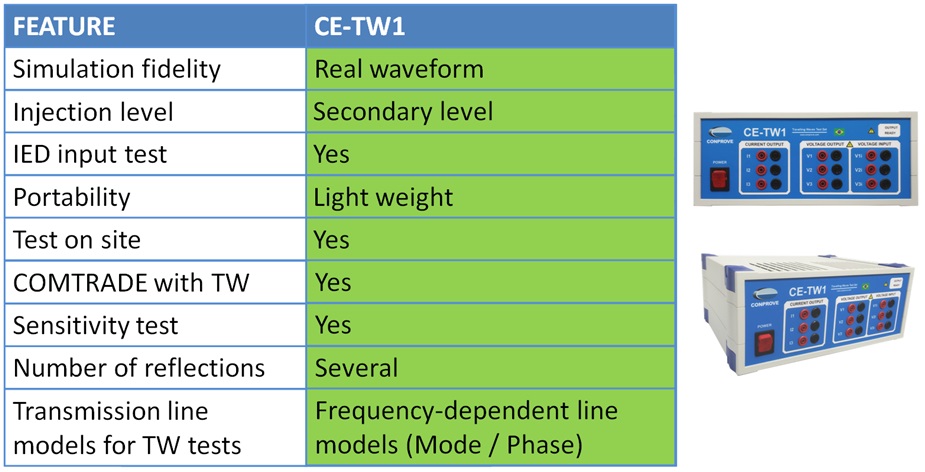
[PT-EN] Ao testar aplicações de Traveling Waves (TW) para localização de faltas e funções de proteção, o sinal simulado é dividido em dois espectros: a baixa frequência sendo gerada por uma mala de testes convencional e a alta frequência sendo reproduzida por amplificadores especiais capazes de responder a um amplo espectro de frequências (DC – MHz). A sincronização é responsável por garantir que não haja escorregamento do sinal.
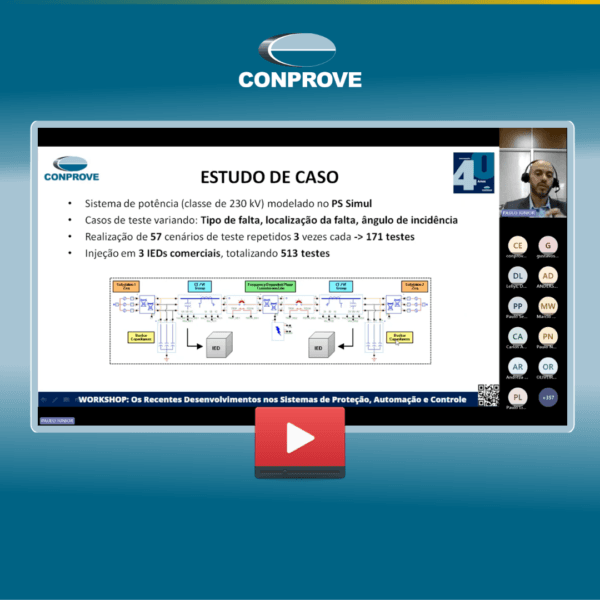
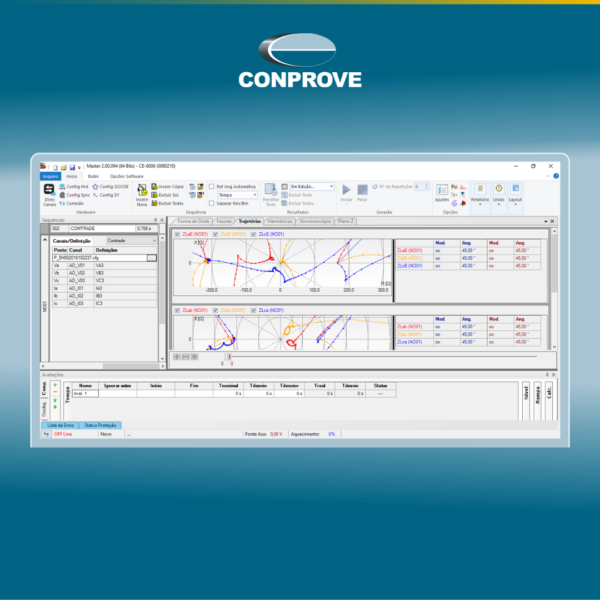
O software PS Simul (desenvolvido no Brasil desde 2009) foi criado com o principal objetivo de permitir ao usuário modelar sistemas complexos de potência e controle, e simular transitórios eletromagnéticos e eletromecânicos, trabalhando com uma interface muito amigável, com uma série de recursos que facilitam a obtenção e avaliação de resultados, entrada de dados, visualização, entre outros. Além de realizar as simulações, o software permite a reprodução/aquisição dos sinais pela mala de testes.
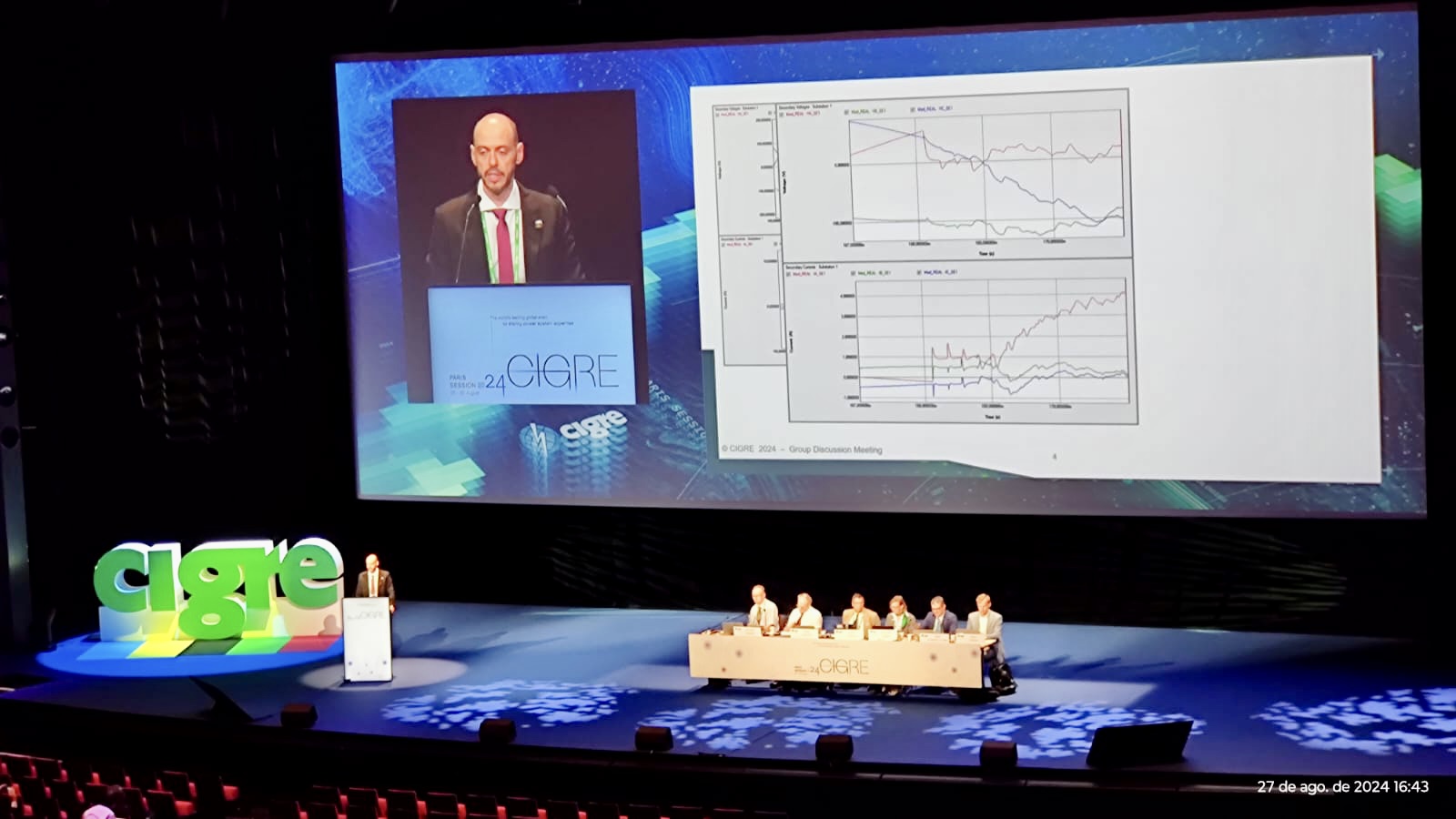
[EN] Presentation of the second contribution of the Special Reports on Traveling Waves at the Cigre Biennial 2024 – Paris/France
In testing applications of TW for fault location and protection functions, the simulated signal is splitted in two spectrums: the low frequency being generated by a conventional test set and the high frequency being reproduced by special amplifiers capable of responding to a wide frequency spectrum (DC – MHz). Synchronization is responsible for ensuring that there are no signal slips.
The PS Simul software (developed in Brazil since 2009) was created with the main purpose of allowing the user to model complex power, control systems and to simulate electromagnetic and electromechanical transients, working with a very friendly interface, with a series of resources that facilitate the obtaining and evaluation of results, data entry, visualization, among others. In addition to carrying out the simulations, the software allows the reproduction / acquisition of the signals by the test set.